

It is the hippocampus that plays a role in this situation.ĭifferent subregions of the hippocampus play an important role in certain types of memory. Simply put, a scent or an image, as well as a melody, can often trigger a memory.
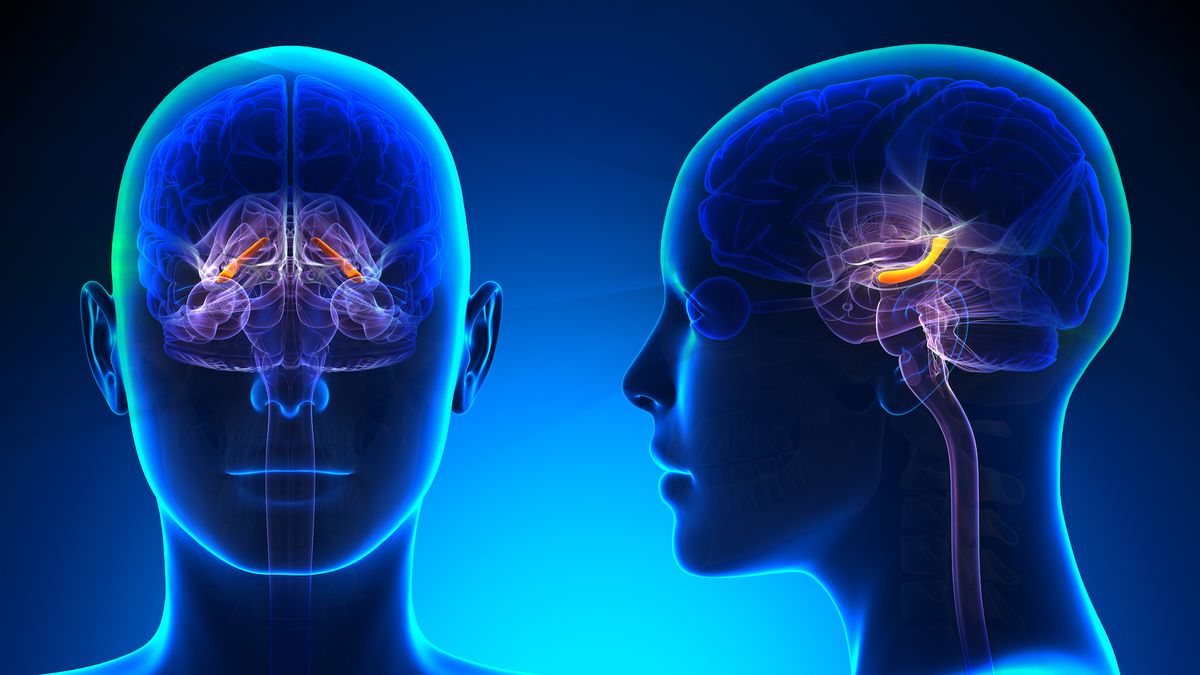
Hippocampus and our MemoryĪs already mentioned, the hippocampus plays a key role in creating, organizing, and storing new memories, as well as connecting some of the feelings and sensations to those memories ( 1). Moreover, the posterior parietal corticesĪre responsible for spatial processing, as well as cognitive processes. The hippocampus, we can say that its orbitofrontal cortex is related to the At the same time, it is not required for semantic memories. The leading theory today says that the hippocampus is necessary for the long-term recall of the context-rich memories. This is the well-known issue of systems consolidation. Do the long-term memories become independent of this part of the brain or not? Is the cortex itself able to perform the memory recall?
#Hippocampus anatomy plus
This theory is contrary to the theory that observes it as memory plus experience reinforced by sensations.įurthermore, scientists disagree about the following issue. Interestingly, this theory says that the hippocampus stores the elements, not the whole experience. You could think of it as a book index that helps us find the information we are looking for in seconds. Some theories say that the hippocampus controls memories through reducing similar experience interference and overlapping, which helps rapid learning processes.Īccording to another theory, the hippocampus is an index of our brain and experiences. Others think that the process resembles a conscious recollection of memories. Some scientists believe that it links memories to experiences and that this is the mode of storing them. However, we still don't know exactly with a 100% certainty of how memory processes happen.

Today, scientists agree that the hippocampus is the key brain center for memory. After thorough hippocampus removal experiments showed that the hippocampus is a center in the brain responsible for forming new memories, both event, and fact-related ones, this theory became more influential. On the other hand, the memory theory hypothesis is somewhat older. As a result, the hippocampus is the key spatial navigation center in our brain. These are the so-called "place fields." This discovery led us to the conclusion that the hippocampus scans the space and maps the environment. These are the so-called " place fields." This discovery led us to the conclusion that the hippocampus scans the space and maps the environment.Īs a result, the hippocampus is the key spatial navigation center in our brain. Namely, these cells reacted when certain locations in space were hit. In 1971, a discovery of the hippocampus cells that burst action potential led to the reinforcement of the spatial theory hypothesis. Those are the theories related to memory and space ( 1). Two of them are the most prominent and the most likely to be correct. Several theories aim to prove the range of the hippocampus functions. It is also related to memory consolidation during sleep. Secondly, it plays a part in the process of linking the sensations to the memories. First of all, the hippocampus is responsible for the formation, organization, and storage of memories ( 1). Moreover, the role of the hippocampus in the limbic system and the nervous system itself is of the utmost importance. The limbic system is the highest part of the subcortical structures responsible for emotions, motivation, instincts, vegetative functions, learning, and memory.Įxcept for the hippocampus, the limbic system consists of the hypothalamus, septal region, limbic bark, the limbic nuclei, including the amygdala, basal forebrain, septal nuclei, anterior thalamic nuclei, and habenula nuclei, as well as the parts of the brainstem and the limbic pathways. This brain structure is a part of the limbic system. It is responsible for the process of transferring the data from the short-term into long-term memory. Hippocampus is one of the key parts of our brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
